一、适用场景 在一张地图中,绘制从起点移动到终点的最优路径,地图中会有障碍物,必须绕开障碍物。
二、算法思路 1. 回溯法得到路径 (如果有路径)采用“结点与结点的父节点”的关系从最终结点回溯到起点,得到路径。
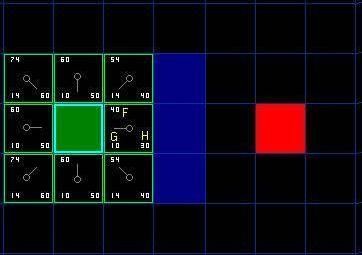
2. 路径代价的估算:F = G+H A星算法的代价计算使用了被称作是启发式的代价函数。从起点到当前结点的实际路径代价 (为啥叫实际?就是已经走过了,边走边将代价计算好了);H表示当前结点到达最终结点的估计代价 (为啥叫估计?就是还没走过,不知道前面有没障碍、路通不通,所以只能用估计);F表示当前结点所在路径从起点到最终点预估的总路径代价 。
G的计算方式:计算方式有挺多种的,这里我们就用这种吧,假设每个结点代表一个正方形,横竖移动距离:斜移动距离=1:1.4(根号2),我们取个整数10和14吧,也就是说当前结点G值=父节点的G+(10或14)。
H的计算方式:估价计算也有很多种方式,我们这里使用“曼哈顿”法,H=|当前结点x值-最终结点x值|+|当前结点y值-最终结点y值|(”||”表示绝对值)。
如下图(图不是自己做的,从网上借来的,自己画的话~…惨不忍睹!)
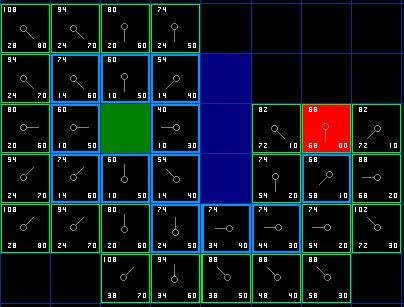
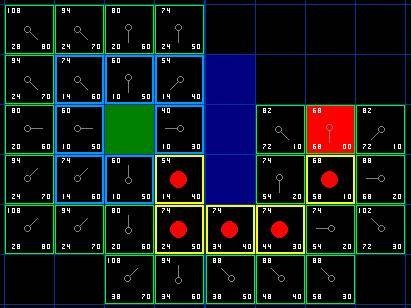
3. 辅助表:Open、Close列表 在A星算法中,需要使用两个辅助表来记录结点。记录可被访问的结点 ,成为Open表;一个是记录已访问过的结点 ,称为Close表。这两个表决定了算法的结束:条件是最终结点在Close表中(找到路径)或Open表为空(找不到了路径)。
4. 移动结点、相邻结点的处理 上面的理解的话,现在就来移动当前的节点,寻找路径。
每次从Open表中取出F值最小的结点出来(这里我们使用优先队列来处理比较好 ),作为当前结点;然后将当前结点的所有邻结点按照邻结点规则 加入到Open表中;最后将当前结点放入Close表中,这里就是每次循环的执行内容。
邻结点规则 :设该邻结点的父节点为当前结点 ;当邻结点在Open表中,我们需要做个比较:如果邻结点的G值>当前结点的G值+当前结点到这个邻结点的代价,那么修改该邻结点的父节点为当前的结点(因为在Open表中的结点除了起点,都会有父节点),修改G值=当前结点的G值+当前结点到这个邻结点的代价
蓝色框框表示在Close表中,绿色的框框表示在Open表中
三、代码实现(Java) 1. 输入 (1) 代表地图二值二维数组(0表示可通路,1表示路障)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 int [][] maps = { { 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 }, { 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 }, { 0 , 0 , 1 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 1 , 1 , 0 , 0 }, { 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 }, { 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 }, { 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 }, { 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 } };
(2) 按照二维数组的特点,坐标原点在左上角,所以y是高,x是宽,y向下递增,x向右递增,我们将x和y封装成一个类,好传参,重写equals方法比较坐标(x,y)是不是同一个。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class Coord public int x; public int y; public Coord (int x, int y) { this .x = x; this .y = y; } @Override public boolean equals (Object obj) { if (obj == null ) return false ; if (obj instanceof Coord) { Coord c = (Coord) obj; return x == c.x && y == c.y; } return false ; } }
(3) 封装路径结点类,字段包括:坐标、G值、F值、父结点,实现Comparable接口,方便优先队列排序。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 public class Node implements Comparable <Node > public Coord coord; public Node parent; public int G; public int H; public Node (int x, int y) { this .coord = new Coord(x, y); } public Node (Coord coord, Node parent, int g, int h) { this .coord = coord; this .parent = parent; G = g; H = h; } @Override public int compareTo (Node o) { if (o == null ) return -1 ; if (G + H > o.G + o.H) return 1 ; else if (G + H < o.G + o.H) return -1 ; return 0 ; } }
(4) 最后一个数据结构是A星算法输入的所有数据,封装在一起,传参方便。:grin:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class MapInfo public int [][] maps; public int width; public int hight; public Node start; public Node end; public MapInfo (int [][] maps, int width, int hight, Node start, Node end) { this .maps = maps; this .width = width; this .hight = hight; this .start = start; this .end = end; } }
2. 处理 (1) 在算法里需要定义几个常量来确定:二维数组中哪个值表示障碍物、二维数组中绘制路径的代表值、计算G值需要的横纵移动代价和斜移动代价。
1 2 3 4 public final static int BAR = 1 ; public final static int PATH = 2 ; public final static int DIRECT_VALUE = 10 ; public final static int OBLIQUE_VALUE = 14 ;
(2) 定义两个辅助表:Open表和Close表。Open表的使用是需要取最小值,在这里我们使用Java工具包中的优先队列PriorityQueue,Close只是用来保存结点,没其他特殊用途,就用ArrayList。
1 2 Queue<Node> openList = new PriorityQueue<Node>(); List<Node> closeList = new ArrayList<Node>();
(3) 定义几个布尔判断方法:最终结点的判断、结点能否加入open表的判断、结点是否在Close表中的判断。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 * 判断结点是否是最终结点 */ private boolean isEndNode (Coord end,Coord coord) return coord != null && end.equals(coord); } * 判断结点能否放入Open列表 */ private boolean canAddNodeToOpen (MapInfo mapInfo,int x, int y) if (x < 0 || x >= mapInfo.width || y < 0 || y >= mapInfo.hight) return false ; if (mapInfo.maps[y][x] == BAR) return false ; if (isCoordInClose(x, y)) return false ; return true ; } * 判断坐标是否在close表中 */ private boolean isCoordInClose (Coord coord) return coord!=null &&isCoordInClose(coord.x, coord.y); } * 判断坐标是否在close表中 */ private boolean isCoordInClose (int x, int y) if (closeList.isEmpty()) return false ; for (Node node : closeList) { if (node.coord.x == x && node.coord.y == y) { return true ; } } return false ; }
(4) 计算H值,“曼哈顿” 法,坐标分别取差值相加
1 2 3 4 private int calcH (Coord end,Coord coord) return Math.abs(end.x - coord.x) + Math.abs(end.y - coord.y); }
(5) 从Open列表中查找结点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 private Node findNodeInOpen (Coord coord) if (coord == null || openList.isEmpty()) return null ; for (Node node : openList) { if (node.coord.equals(coord)) { return node; } } return null ; }
(6) 添加邻结点到Open表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 * 添加所有邻结点到open表 */ private void addNeighborNodeInOpen (MapInfo mapInfo,Node current) int x = current.coord.x; int y = current.coord.y; addNeighborNodeInOpen(mapInfo,current, x - 1 , y, DIRECT_VALUE); addNeighborNodeInOpen(mapInfo,current, x, y - 1 , DIRECT_VALUE); addNeighborNodeInOpen(mapInfo,current, x + 1 , y, DIRECT_VALUE); addNeighborNodeInOpen(mapInfo,current, x, y + 1 , DIRECT_VALUE); addNeighborNodeInOpen(mapInfo,current, x - 1 , y - 1 , OBLIQUE_VALUE); addNeighborNodeInOpen(mapInfo,current, x + 1 , y - 1 , OBLIQUE_VALUE); addNeighborNodeInOpen(mapInfo,current, x + 1 , y + 1 , OBLIQUE_VALUE); addNeighborNodeInOpen(mapInfo,current, x - 1 , y + 1 , OBLIQUE_VALUE); } * 添加一个邻结点到open表 */ private void addNeighborNodeInOpen (MapInfo mapInfo,Node current, int x, int y, int value) if (canAddNodeToOpen(mapInfo,x, y)) { Node end=mapInfo.end; Coord coord = new Coord(x, y); int G = current.G + value; Node child = findNodeInOpen(coord); if (child == null ) { int H=calcH(end.coord,coord); if (isEndNode(end.coord,coord)) { child=end; child.parent=current; child.G=G; child.H=H; } else { child = new Node(coord, current, G, H); } openList.add(child); } else if (child.G > G) { child.G = G; child.parent = current; openList.add(child); } } }
(7) 回溯法绘制路径
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 private void drawPath (int [][] maps, Node end) if (end==null ||maps==null ) return ; System.out.println("总代价:" + end.G); while (end != null ) { Coord c = end.coord; maps[c.y][c.x] = PATH; end = end.parent; } }
(8) 开始算法,循环移动结点寻找路径,设定循环结束条件,Open表为空或者最终结点在Close表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public void start (MapInfo mapInfo) if (mapInfo==null ) return ; openList.clear(); closeList.clear(); openList.add(mapInfo.start); moveNodes(mapInfo); } * 移动当前结点 */ private void moveNodes (MapInfo mapInfo) while (!openList.isEmpty()) { if (isCoordInClose(mapInfo.end.coord)) { drawPath(mapInfo.maps, mapInfo.end); break ; } Node current = openList.poll(); closeList.add(current); addNeighborNodeInOpen(mapInfo,current); } }